DARK SPOTS CAN LEAD TO PHOTO AGING
In Brightening
We know the importance of protecting our skin from the sun. After all, we see our skin get darker when we bask in the sun and we also know that too much sunshine burns our skin. But what does over-exposure to the sun really do to our skin?
Over-exposure to the sun can cause hyperpigmentation, dark spots and dull skin. According to the skin experts at The Pond’s Institute, it can eventually lead to a process known as photo aging. Read on as the experts shine more light on the science behind photo aging.
Photo aging is a sign of UV damage on your skin.
What is photo aging?
Photo aging refers to the process that your skin undergoes when constantly overexposed to harmful UVA and UVB rays. This can eventually give your skin a darkened, leathery appearance.
How does photo aging happen?
Photo aging begins with the sun. UVA and UVB are invisible but harmful rays that come from the sun. As part of our skin’s self-defence mechanism, the melanocytes in the dermis layer of our skin produce melanin to protect cells from damage. Melanin causes skin to naturally tan. Melanin may also over-produce when skin cells are inflamed.
Skin produces melanin to counter UV damage. But overproduction of melanin can disrupt the natural melanin production process.
While melanin may be our skin’s primary self-defence mechanism, its over production deep inside can lead to uneven tone and dark spots outside. Over time, these spots within the skin will have disrupted optimum melanin production and cause a chronic process of melanin overproduction.
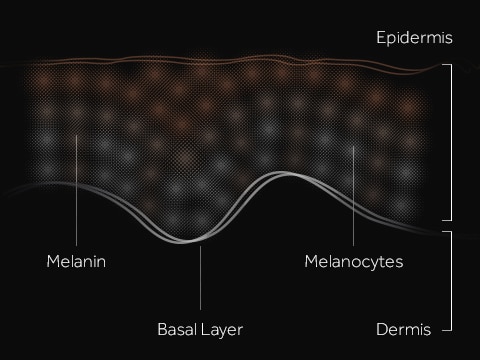
Since the melanocytes are stuck producing melanin over and over again, these melanin are transferred to the surrounding cells and get stuck in the epidermis and appear not shed away with the daily skin renewal process.
This appears on your skin’s surface as uneven skin tone and darkened skin. At this stage, if your skin continues to be exposed to UVA and UVB rays, then, photo aging occurs deep inside and your skin takes on a spotted and leathery appearance on the outside.
What’s so bad about photo aging?
Photo aging is a result of UV damage in your skin. UV damage causes skin cells to release enzymes that lead to more damage. The fibroblasts in your dermis unwind and become disorganized. This weakens the internal support structure of your skin.
If UV-damaged skin continues to be exposed to more sun, the photo aging process occurs.
When the internal support structure of skin collapses, the dermis becomes thinner and starts to sag. Meanwhile, the elastin and collagen in your skin begins to degenerate as a result of UVA injury. All this accumulated damage makes skin visibly less firm, less supple,and cause solar elastisis— the loss of elasticity in skin, making it difficult for the skin to renew itself.
When this prolonged sun-exposure damage continues over time, photo aging goes into hyperspeed, causing more damage in your skin.
Thankfully, there are ways to prevent the appearance of dark spots and other photo aging process in your skin. Read more to find out how you can prevent the damage on your skin or learn about the other causes of dark spots in your skin.

